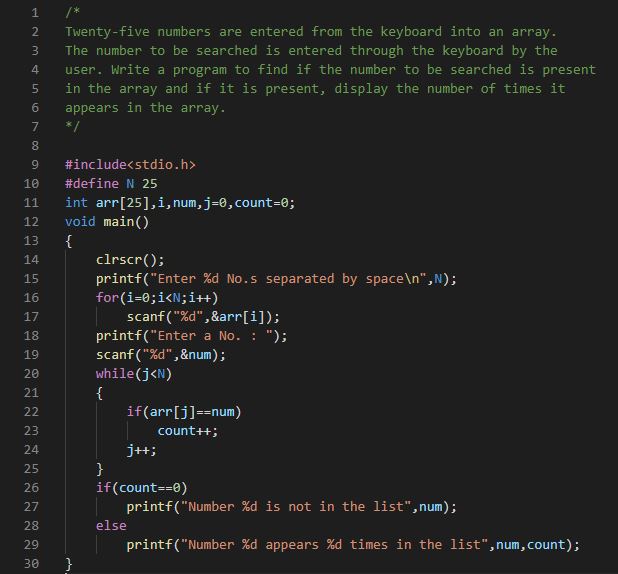
Let Us C (Chapter 8 : Arrays) : Program-13_3

(3) Write a program to sort a 4 x 4 matrix . // Let Us C (Chapter 8 : Arrays) : Program-13_3 /* (3) Write a program to sort a 4 x 4 matrix. */ #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int M1[4][4],i,j,k,smallest,temp,*arr; clrscr(); printf("\nProgram to sort elements of a 4x4 Matrix"); printf("\nEnter 4 X 4 matrix"); printf("\nEnter 16 elements of 4x4 Matrix separated by space\n"); for(i=0;i<4;i++) { for(j=0;j<4;j++) { scanf("%d",&M1[i][j]); } } printf("***** Entered Matrix is *****\n"); for(i=0;i<4;i++) { for(j=0;j<4;j++) { printf("%4d",M1[i][j]); // print matrix } printf("\n"); } arr = M1; // Copy matrix for(i=0;i<15;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<16;j++) { if(*(arr+i) > *(arr+j)) { temp = *(arr + i); *(arr + i) = *(arr + j); *(arr + j) = temp; } } } printf("***** Sorted Matrix is *****\n"); for(i=0;...